Pull-up & Chin-up Guide | How to do Pull-ups & Chin-ups
Apr 21st, 2010 - written by Stephan in Strength Training
(0 comments)
Without doubt, pull-ups and chin-ups are one of the most effective basic exercises to develop a muscular upper body. They work a large number of muscles simultaneously and, through different grip setups and techniques, offer many different training variations.

Pull-up Benefits
| Strength | Pull-ups are a great exercise to strengthen almost all upper body and arm muscles, including the hand's gripping strength. |
|---|---|
| Muscles | Doing Pull-ups on a regular basis can develop an impressive upper body. |
| Balance | Pull-ups help maintaining the upper body's muscular balance by compensating the popular pressing exercise for chest and front shoulders. |
| Simplicity | Pull-ups require nothing but a fixed horizontal bar or something similar to grasp. Once you're able to perform a few pull-ups, you can train virtually anywhere. |
| Versatility | A variety of grip setups and many training techniques make pull-ups a versatile and interesting exercise. |
Basic Pull-up Instructions
- Stand below pull-up bar and grasp it with wide overhand grip. Hang on bar.
- Bend your knees and cross your lower legs.
- Pull your body up until your upper chest reaches the bar. Look up and keep chest up, leading toward the bar.
- Return with same speed. Keep the arms very slightly bent at the bottom of the motion to maintain the muscular activity. Simultaneously let your your shoulders be pulled up by the bodyweight.
- Repeat.
The Difference Between Pull-ups and Chin-ups
While the basic pulling movement is the same, pull-ups and chin-ups differ in the hand's grip setup.| Pull-ups | Chin-ups |
|---|---|
 |  |
| Palms facing away from you involves less arm flexor muscles and more back. It is harder. | Palms facing you involves less back muscles and more arm flexors. It is easier. |
Pull-up Techniques
Especially for beginners pull-ups a are a major challenge. Not only do they require a good relation of strength and bodyweight, but also a very specific muscular coordination that can only be improved by doing it.Don't stick to Lat Pull-downs for too long. Even if you're strong enough to sit and pull down about your bodyweight, it doesn't mean you're able to do a single correct pull-up, because you're not accustomed to the specific technique. Any great performance on the pull-up bar comes from hard and consistent training.
Beginner's Techniques
| Lat Pull-downs |  |
|
|---|---|---|
| Assisted Pull-ups, Machine |  |
|
| Assisted Pull-ups, Elastic Band |  |
|
| Assisted Pull-ups, Training Partner |  |
|
| Negative Pull-ups | 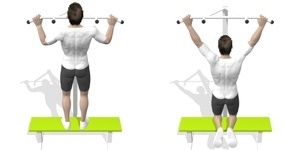 |
|
| Partial Repetitions |  |
|
Advanced Techniques
| Weighted Pull-ups |  |
|
|---|---|---|
| Slow Negatives | 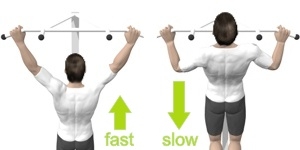 |
|
Pull-up Variations
| Wide Overhand Grip |  |
|
|---|---|---|
| Close Overhand Grip |  |
|
| Neutral Grip |  |
|
| Close Neutral Grip |  |
|
| Reverse Grip |  |
|
| Wide Reverse Grip |  |
|
| Mixed Grip |  |
|
| One Arm Reverse Grip |  |
|
Common Mistakes
- Straight Arms. Extending the arms completely disables all major muscular activity for a moment, which may result in overstressed passive structures, such as tendons and ligaments.
- Swinging. Try to keep hips and legs as stable as possible. Don't kick legs and don't swing back and forth.
Exercise Guide Links to Pull-ups & Chin-ups
Pull-upPull-up, Assisted
Pull-up, Behind Neck
Pull-up, Close Grip
[linkexercise]bodyweight_v_grip_pull_up[/linkexercise]
Chin-up
... read more
10 Simple Strategie For Gaining Muscle Mass
Mar 18th, 2010 - written by Stephan in Strength Training
(0 comments)
1. Increased Muscular Tension
The conscious flexion of the working muscles over the entire range of motion causes an increased muscular stimulation. This technique particularly suits isolation exercises.
Thus, for example when doing Arm Curls, an extra tightening of the arm flexing muscles at the end of the concentric phase will increase the stimulus to the biceps.
In general, the eccentric part of a movement should be done slowly and deliberately under high muscular tension, which in turn leads to a higher training level, a more intense workout and an improved development of strength and muscle mass.
2. Final Contractions
Final contractions can lead to up to 30% increased muscular stimulation. Simply do 3-5 partial repetitions with almost extended joint positions after finishing a set.For example, after the last repetition of the lat pull-down exercise, before dropping the weight, do a few repetitions in the upper part of the movement. You can apply this technique to almost any strength exercise.
3. Train Complex
A high and complex effort, and thus progressively higher workload is critical to muscular development.You can move the highest weights during basic compound exercises that stimulate many muscles simultaneously and that involve functional movements.
| Complex Exercises For The Upper Body | Complex Exercises For The Lower Body |
|---|---|
|
|
4. Train Standing
Try to do as many exercises as possible in standing position, because it requires and triggers the development of a larger number of stabilizing muscles, especially core muscles.It is important to keep up a correct training technique and to avoid any swinging. This is particularly suitable for the training of the shoulders and arms, for example, Shoulder Presses with Barbell or Dumbbells, Lateral Raises, Arm Curls and Triceps Extension.
3. Variation: Heavy - Light - Heavy
To build muscles, it is important to use heavy weights and to train a the range of 5-8 repetitions.However, muscles need some training variety to constantly develop and to grow.
Switch between heavy load training on the one hand and training with lighter weights on the other. Performing many repetitions with relatively light weights leads to better blood circulation within the affected muscles, resulting in an improved oxygen and results nutrient supply and thus promotes muscle growth.
A very simple and effective method is a permanent heavy weight training in combination with a once per weekly high-rep workout for all major muscle groups.
5. Effective Resting
In order to complete the necessary training volume in minimum time you may want to take advantage of the breaks between sets.Here you either train the corresponding antagonist or any weaknesses, such as Calves or Abdominal Muscles.
Short and intense workouts cause a higher production of hormones that are involved in muscle building.
6. Eat More
To gain weight, you need to take in more energy than you consume. Therefore you need to eat more and you need to eat the right food.To maximize the calorie intake eat mainly foods with a high energy density. Foremost amongst these are healthy fats such as olive oil, canola oil, nuts and peanut butter.
In addition, a sufficient supply of proteins is important. If you cannot meet the daily requirements through diet, it makes sense to resort to supplements, such as protein shakes.
If you are not able to take in large enough amounts of calories through solid food, you need to drink more energy-dense fluids. Drink plenty of milk, preferably whole milk, since the combination of protein and a little more fat leads to a longer digestion time in the stomach, and thus provides more energy of a longer time. Otherwise, high-calorie juices and self-made smoothies, such as milk with oatmeal and fruits, prepared in mixer, are an excellent source of energy.
7. Drink More
Muscles consist to 65% of water. Your muscles won´t grow without a sufficient water supply.The complete protein and fat metabolism is based on an adequate fluid intake. To effectively build muscle mass, you need to dink 1 liter of water per day per 20 kg of body weight.
8. Rest More
Reduce the calorie consumption besides the strength training to a minimum. Avoid long cardio units.Train hard and be lazy for the rest of the day. To ensure a good recovery and muscle growth you need to sleep about 8 hours per night.
9. Eat Directly After Training
After each intense workout, the muscles are hungry for glycogen and amino acids. Fulfill these needs promptly.To make the most of the time window of about 15 minutes, you should either have a full meal, or alternatively drink a whey protein shake together with with rapidly digestible carbohydrates.
10. Think BIG
Ultimately, it is important to be convinced of your own performance and muscle growth.Imagine to already own the desired muscles. Visualize it every day. The right mental cinema provides the necessary motivation.
Set the right priorities in terms of muscle building and developing a certain unwillingness to compromise, that is do everything necessary to reach your goal and to avoid any actions that prevent you from growing muscles.
... read more
Nutrition 101: How much Protein per Day
Feb 4th, 2010 - written by Stephan in Nutrition
(0 comments)
The recommended amount of protein per day is a hot topic, especially among strength training athletes, that is steadily revived by confusing recommendations in so-called professional journals and other media.
Meanwhile, there are studies, one I will look at here in detail, that support my personal experience in terms of training, nutrition and muscle-building. But before that, let me clarify a few terms and issues around the subject of protein.

Ei. Image credit by mac.black
What is Protein?
Proteins are usually denoted as the building blocks of life. They are composed of amino acids, which in turn are the basic building block of all cells in the body. In addition to the structure building tasks, amino acids are responsible for a variety of other bodily functions such as oxygen and iron transport in the blood, the formation of antibodies and the secretion of hormones. In short, no life without proteins. The continuous cell degradation and recovery processes in the body demand the daily intake of a certain amount of protein through diet. Even physically inactive people have to cover a basic need for protein.The Daily Requirement
As the level of physical activity increases, through an intense strength or endurance training for example, the demand for protein is growing equally, since the related metabolic processes of regeneration and adaptation of the body to the higher level of physical activity ask for more amino acids. But the disproportionately large amounts of protein, which are particularly recommended by many athletes, professional journals and the nutritional supplement industry, cannot be justified by that.The "How much protein should I eat per day" table:
| Type of Physical Activity | Daily Amount of Protein per Pound Body Weight |
|---|---|
| Inactive | 0,5 gram |
| Endurance Training | 0,75 gram |
| Strength Training | 1 gram |
These numbers cover the daily need. The significant and deliberate exaggeration of the recommended amounts of protein for the particular activity level as well the amount of protein served per meal offer, according to a study mentioned on www.medicalnewstoday.com the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, no significant benefits and even generate some unwanted side effects. “Most of the excess is oxidized and could end up as glucose or fat.”
The Right Timing and the Right Amount
Tests during this study have shown that the intake about 30 grams of protein per meal provides an ideal supply with amino acids to make sure the muscle synthesis. Among the volunteers who have taken up to 90 grams of protein per meal, no further increase in muscle protein could be demonstrated. Consequently the daily amount of protein has to be distributed fairly evenly among several meals throughout the day. Again, the researchers from Texas offer some interesting insights. Thus, the recommendation is to take in the first 30 grams of protein as early as breakfast and to cut the amount somewhat in the evening, as the synthesis of muscles functions most effectively during the day, while at night no significant amounts of protein can be processed.Conclusion
Therefore the uncontrolled intake of large amounts of protein, especially in the field of strength training and bodybuilding, is just a curiosity. Replaced it by an intelligent handling of the own food and potential supplements. My own experiences has shown that an intensive weight training, which primarily targets developing strength and muscle density and not large muscular volume, is agreeable with a long-term protein intake on the level of an endurance athlete, that is below the mentioned 1 gram per pound body weight. Source: http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/168876.php... read more
Training 101: Machines or Free Weights?
Jan 27th, 2010 - written by Stephan in Strength Training
(0 comments)
Introduction
Basically strength training is done either with free weights, mostly dumbbells, barbells and several variations of the barbell, or with machines. A balanced training routine offers enough room for both, free weights and machines. However, for an effective muscle growth or strength training you should prefer the use of free weights. Here´s why?
Machines
Machines are designed to offer a pre-defined training direction and sometimes even range of motion. Stabilizing the training weight and the own body weight and is mostly taken by the machines. Consequently you train only the necessary muscles. This type of training is very specific; it is simple to do and bears only low potential for error and injury. The major disadvantage is the limited complexity and thus effectiveness. What does that mean? The degree of complexity of an exercise, in large part, determines the training effect. The more muscles you involve in a movement, directly or indirectly, the higher the overall training stimulus will be. Here three terms come into play:| Target Muscle | the major group of muscles involved in an exercise |
|---|---|
| Synergists | they support the movement directly |
| Stabilizers | contracting muscles with no significant movement to fixate joints or to maintain a certain posture |
While training on machines, you usually involve only agonists and synergists, stabilizers play only a small role.
Free Weights
Unlike when using free weights. Here, too, in principle, each exercise follows a defined movement, but it is solely the responsibility of the athlete to do a correct technique, to fixate the body in an ideal position and to stabilize the training weight. Free weight training improves the co-ordination skills and body awareness, and represents a great physical challenge in its complexity in the interplay between directly and indirectly involved muscle groups, with greater potential for development.Conclusion
As initially mentioned, the use of machines offers an entirely adequate training. However, when it comes to the basic development of strength and co-ordination or a balanced growth of muscle mass, the use of free weights is the smarter choice.... read more
Push-ups: Correct Training Technique and Variations
Jan 17th, 2010 - written by Stephan in Strength Training
(0 comments)
Introduction
Without doubt push-ups are the most popular bodyweight exercise. They strengthen almost the entire body, especially chest, shoulders and arm muscles, they are available in many variations, you can do them without any equipment and the technique is quite easy to learn. Yet, it takes some basic knowledge to do push-ups correctly, because like with any other strength training exercise, also push-ups bear the potential of mistakes that may lead to injuries and pains. Therefore read this guide to a correct push-up training technique.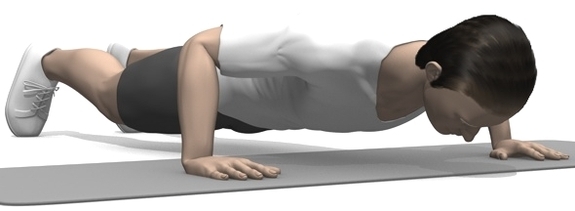
Push-up Benefits
| Strength | Working with your own bodyweight requires great effort and makes push-ups the a perfect exercise for strengthening the muscles of the torso. |
|---|---|
| Muscle Growth | Anyone who does push-ups on a regular basis may soon be pleased to develop some muscles. Push-ups mainly build chest, front shoulders and triceps muscles. |
| Effectiveness | Besides the dynamically active muscles push-ups also put high demand on many stabilizing muscles, which an almost total body workout out of this exercise. |
| Simplicity | A great advantage is the simplicity of push-ups. You can do push-ups almost anywhere and anytime. |
Push-up Technique
- Place your hands slightly more than shoulder-wide apart on the floor.
- Then extend you body, place feet with toe tips on floor as well and hold your body above the floor while keeping your arms almost extended.
- Now bend your elbows and lower your body until the chest almost touches the floor and your elbows are bent about at right angles.
- Press your body up into the starting position, elbows remain slightly bent.
- Repeat as often as possible, provided a correct training technique.
Push-up Setup
| Hands | Place the hands slightly wider than shoulder-wide apart, not too far away. Let the fingertips point forward. |
|---|---|
| Wrists | Placing the palm flat on the floor can occasionally lead to pain within the strongly extended wrists. In this case, it is better to do the push-ups on the fists or with handles, which allows the wrists to stay straight. |
| Upper Arms | Hold your upper arms between almost perpendicular to the upper body or close to the upper body, depending on the type of push-up. |
| Waist | Keep the abdominal muscles tight. Shoulders, hips and ankles form a straight line. Do not allow the body to sag. |
| Glutes | Also keep the gluteal muscles tight. Along with the abdominal tension it prevents the body from sagging. |
| Head | Keep the head aligned to the spine in a neutral position and look down. |
Push-up Variations
There are a variety of push-up variations that make this exercise either lighter or heavier or have that shift the demand on different muscles involved.| Name | Image | Target Muscle | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Push-up |  | Pectoralis Major, Sternal | Push-up |
| Push-up, Close Grip |  | Triceps Brachii | Push-up, Close |
| Push-up, incline |  | Pectoralis Major, Sternal | Push-up, Incline |
| Push-up, decline |  | Pectoralis Major, Clavicular | Push-up, Decline |
| Push-up, Diamond |  | Triceps | Push-up, Diamond |
| Push-up, with Elastic Band |  | Pectoralis Major, Sternal | Push-up |
| Push-up, on Knees |  | Pectoralis Major, Sternal | Push-up, On Knees |
| Push-up, One Arm |  | Pectoralis Major, Sternal | Push-up, One Arm |
Common Mistakes
| Overextended Wrists | As mentioned before, some people may experience pain from overextended wrists. In this case it is better to perform the push-ups on the fists or with special push-up grips. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sagging body | . | ||
| Head Leading | During push-ups keep neck and head aligned to the body. Move your chest to the ground and let your head follow the motion. | ||
| Looking ahead | To avoid unfavorable strains or injuries in the neck, it is very important to look down in a neutral fashion while doing push-ups. | ||
| Upper Arm Abduction | For the shoulder joints secure the upper arm angles are between slightly below perpendicular to the body and near besides the body. |
... read more

