The Metabolism
As mentioned before, our metabolic performance has great influence on our life, and vice versa. Of course, the metabolic rate itself is as individual as every person, but there are several internal and external factors that determine how well it is doing.Surprisingly, genetic conditions, with just 5% share, have only minor influence on the metabolic rate. Therefore "bad" genetics don´t deliver a plausible explanation for a low metabolic rate
It is rather age, sex and lifestyle that influence the metabolism. The first two factors we have to accept as they are. From the age of 25 on the bodies energy requirement underlies an annual decrease of 1%, which means that during an adults lifespan the metabolism decreases by up to 40%.
Fortunately, this process can be delayed and even turned around by the third factor: living an active lifestyle has a positive effect of the body´s entire energy demand, even in the state of rest.
The following chart shows the most substantial metabolic rate influences.
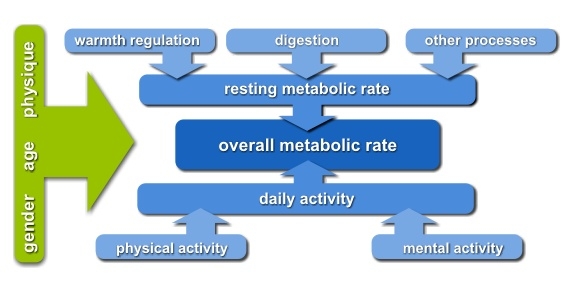
Simplified the total energy consumption is calculated as follows:
Complete Energy Turnover = Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) + Energy used by Activities
The Basal Metabolic Rate is the body´s energy demand in absolute rest, which makes up about 60% of our complete energy turnover. Physical activity itself demands about 30% and temperature regulation about 10%.

Concluding, a long-term and successful metabolic rate increase is mainly based on an improved BMR. There are many other possibilities, besides physical activity, to affect the the BMR in a positive way.
1. Regular Strength Training
Muscles are active body mass. They burn energy even at rest, during physical activity the become fat burning furnaces that burn plenty of energy.Excess body fat can only be burnt inside the muscles, no place else. The more muscles you have, the higher the chance of having an optimum body fat percentage.
After lifting weights the BMR remains on a high level for the next 48 hours. Therefore working out 2-3 times per week causes a permanently increasing energy demand, day and night.
2. Cardiovascular Training
Cardiovascular Training has a far less influence on the BMR..Aerobic exercise with a heart rate of about 65% of your MHR (maximum heart rate) burns about 300-400 kcal per hour. It would take almost three hours of low intensity cardiovascular training per week to balance one larger meal.
Also, after cardio training the BMR remains on a high level for only about 1-2 hours, which is much less in comparison to strength training.
However, endurance is also an important part of the battle. It can be done on a regular basis without a great deal. Especially short, but intense training sessions or interval trainings of aerobic and an-aerobic exercise burn plenty of energy.
3. Daily Activity
Abandon many of your everyday comforts to increase your energy demand.- Instead of using the car go by bike or walk short distances.
- Recognize even the smallest stairs as a short training session. Avoid elevators and escalators whenever possible.
- When sitting, get up at least once per hour and move. Maybe carry out tasks that require you to visit other floors or different departments.
- Be active whenever possible, even home works burns a lot of calories.
- Pick sporting hobbies, e.g. in team and ball sports.
4. Mental Activity
The brain makes up about 3% of our body weight, but burns 25% of our resting energy. In contrast to muscles, the brain can only burn carbohydrates (glucose).Since the brain can´t store energy, it has to take carbohydrates from the body´s storages.
Demanding mental processes do consume much of the daily fed carbohydrates. Since the body wants to compensate this by an increased carbohydrate intake, mental activity is one major cause of cravings for sweets.
It is not possible to achieve a long-term increase in energy demand, but since mental performance is similar trainable as physical, they are good way to burn a little more energy each day.
5. Eating and Drinking
To maintain a high level of physical energy, you need to eat on a regular basis.Have a small or medium meal every 3-4 hours. Doing this indicates a good supply situation and encourages the body to burn its energy storages (excess body fat).
However, what counts for training also counts for nutrition: Keep boredom at bay!
Ultimately you only may want to watch only your weekly energy balance. A long-term energy surplus leads to gaining weight, a long-term energy deficiency causes weight loss. Seek for an energy balance to maintain your bodyweight. The daily calorie intake should be subject of specific variations to not get your metabolism used to a certain energy level. Keep it interesting
Because almost all metabolic functions require water, drink a sufficient amount of fluid each day. 2-3 liters are a good estimation.
6. Heat
For most people an ambient temperature of 68-73°F is most convenient. Try to escape this area as often as possible, because then the body will have to use energy to balance its temperature.Going to the sauna or taking hot baths are great examples for sources of external heat.
You can also put heat inside your body by drinking hot drinks or by eating hot meals, but beware to not burn your mouth.
7. Coldness
What is true for heat is even more true for coldness.Have cold showers in the morning or have cold baths to push your metabolism. It will wake you up and costs lots of energy.
Don´t dress with too warm clothes. Rather leave it to the body to control its temperature.
Keep the room temperature below 70°F, which encourages your body to move and to maintain a certain level of physical activity to produce warmth.
Have cold food and, even better, cold drinks. Especially ice water, sipped over a longer period of time, is an ideal metabolism booster.
8. Spicy Food
Spicy food can also increase the metabolism.You can recognize it when people begin to sweat while having a spicy meal. It is helpful, although it is not the perfect option.
9. Sleep
Sleeping too little may cause your BMR to slow down, because the body is likely to suffer from poor recovery.Sleep for 6-8 hours every day and try to get up in time without an alarm clock, which may require you to go to bed earlier.
Basically, start the day very early in the morning. Sleeping for too long , way longer than 8 hours, is also counterproductive and makes it hard for your metabolism to rise over the day.
10. Other Extremes
In general, all time your spend outside the everyday comfort zones are stimulating the metabolism.As already mentioned things like heat and cold an important role, but also hormone-releasing states such as pleasure, fun, fear, or (positive :-) excitement. Add several of these ingredients into your daily routine and your metabolism has every reason to remain at a high level.
« back

